|
Acer saccharum Marshall Sugar maple
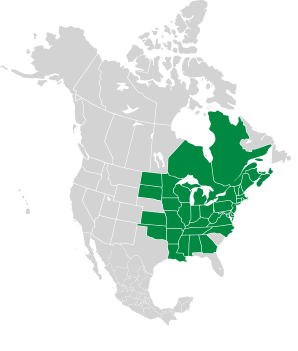
Sugar maples are famous for their clear-running sap, tapped each year in the New England area to produce maple syrup. Real maple syrup, not the fake stuff made with corn syrup that is sold in most grocery stores. There is no comparison! They also produce a light-colored, fine-grained durable wood that is prized for furniture. And they are amazingly beautiful in the fall. Plants: Trees are deciduous, reaching 80-115′ (24-35 m) in height, rarely up to 150′ (45 m). Leaves: Leaves are palmate, up to 8″ (20 cm) in size. Sugar maples are similar to Norway maples, but the leaves have more teeth. Sap from the base of a leaf stem is clear, vs. milky in Norway maples. Silver maples (with the similar-sounding name Acer saccharinum) have much more deeply lobed leaves (both species are found in about the same range). Black maples have leaves with 3 lobes and softer curves. Florida maples have leaves with velvety undersides and more rounded leaf tips, while sugar maples are not hairy. Florida maples are also found predominantly in Alabama, Mississippi, and Georgia (and some parts of Florida and nearby states), while sugar maples occur throughout much of the eastern United States. Flowers: Flowers are in panicles of five to ten, yellow-green, and lacking petals. Trees don’t start producing flowers until they are at least ten years old. Fruits: The seedpods of Norway maples are almost completely opposite each other, while they typically form an angle of about 120° in sugar maples. The “wings” of the seeds, called samaras, are ¾-1″ (2-3 cm) long, with seeds that are ¼-⅜″ (7-10 mm) around. Sugar maples, like this one in southern Maine, are among the most colorful of trees in the fall. Edibility: The sugary sap is boiled down to make maple syrup, a delicacy. Other portions of this tree are not edible. Online References:
Earl J.S. Rook's Flora, Fauna, Earth, and Sky ... The Natural History of the Northwoods The University of Florida Environmental Horticulture site The Ohio State University PLANTFacts database The USDA Forest Service's Silvics of North America site The Virginia Tech Department of Forest Resources and Environmental Conservation The Lady Bird Johnson Wildflower Center Plants for a Future, a resource and information centre for edible and otherwise useful plants 8/7/2017 · Groton Rail Trail, Groton Center, Groton, Massachusetts · ≈ 6 × 4″ (16 × 11 cm)
Acer saccharum description by Thomas H. Kent, last updated 6 Dec 2020. © FloraFinder.org. All rights reserved. |
8/14/2009 · Nashua River Rail Trail, East Pepperell, Massachusetts · ≈ 11 × 7″ (27 × 18 cm) 9/7/2020 · Calderwood Trails, Freeport, Maine · ≈ 7 × 4½″ (18 × 12 cm) 9/7/2020 · Calderwood Trails, Freeport, Maine · ≈ 4 × 6″ (11 × 16 cm) 5/22/2010 · Garden in the Woods, Framingham, Massachusetts · ≈ 14 × 9″ (34 × 23 cm) 11/15/2011 · Nashua River Rail Trail, Groton Center, Groton, Massachusetts · ≈ 3½ × 5″ (9.2 × 13 cm) 9/7/2020 · Maquoit Bay Conservation Area, Brunswick, Maine · ≈ 10 × 6″ (24 × 16 cm) 8/7/2017 · Groton Rail Trail, Groton Center, Groton, Massachusetts · ≈ 6 × 4″ (16 × 11 cm) 8/14/2009 · Nashua River Rail Trail, East Pepperell, Massachusetts · ≈ 11 × 7″ (27 × 18 cm) Range:
|