|
Capsicum annuum ‘Explosive Ember’ Ornamental pepper
Cayenne peppers are natives of southern North America and northern South America. Most of the peppers we eat or grow as ornamentals are cultivated from this species, including anchos, banana peppers, cayennes, de árbols, guajillos, jalapeños, anaheims, Italian sweets, pasillas, peperoncinis, pimentos, poblanos, serranos, and tabascos. (A few, habaneros among them, have other origins.) The 'Black Pearl' cultivar was developed by the U.S. National Arboretum, as an ornamental plant. If you are curious as to the origins of cayenne peppers, consider Kraig Harris Kraft's 2009 dissertation on the subject, The domestication of the chile pepper, Capsicum annuum: Genetic, ecological, and anthropogenic patterns of genetic diversity.
Identification: These peppers are perennials in warm climates, but they must be replanted from seeds in cooler climes. They are 10-14″ (25-35 cm) high, and 8-10″ (20-25 cm) around. New foliage is bright purple. Leaves are oblong-ovate, ovate, or ovate-lanceolate, about 1-2″ (2.5-5 cm) long, and black. Flowers are white and purple. Fruits are bright red, about ¾-1″ (1.9-2.5 cm) long, generally upward-pointing. Edibility: Like most small chili peppers, these are edible and very hot—about 30,000 Scoville units—in the range of tobasco. (Note: not all ornamental peppers are edible though.) Online References:
Nature’s Best Masked Flower Images CalPhotos (Capsicum annuum) The Lady Bird Johnson Wildflower Center (Capsicum annuum) Wikipedia (Capsicum annuum) EFloras (Capsicum annuum) References:
Capsicum annuum ‘Explosive Ember’ description by Thomas H. Kent, last updated 25 May 2020. © FloraFinder.org. All rights reserved. |
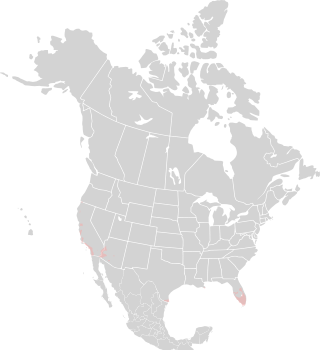
9/7/2010 · Tower Hill Botanic Garden, Boylston, Massachusetts · ≈ 8 × 12″ (20 × 31 cm) Range: Zones 10-11:
|